- Muscle relaxants (e.g., eperisone, tolperisone), magnesium, calcium, and other over-the-counter (OTC) medicines or dietary supplements are commonly used.
ABOUT US
PIPELINE
IR
COMMUNITY
PIPELINE>Fisrt in class
Fisrt in class
BICHEDAM’s Innovative Pipeline
BICHEDAM's BCD101
BCD101 is a herbal composite material developed from six medicinal plants, including those from the Daegu–Gyeongbuk region. It is manufactured in GMP- and HACCP-certified facilities, ensuring the highest standards of quality and safety.
Through collaborative research with regional institutions, including the Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine and the Korean Medicine Advancement Center, its safety, efficacy, and standardization have been fully validated. In addition, BCD101 holds patents related to improving blood circulation.
BCD101
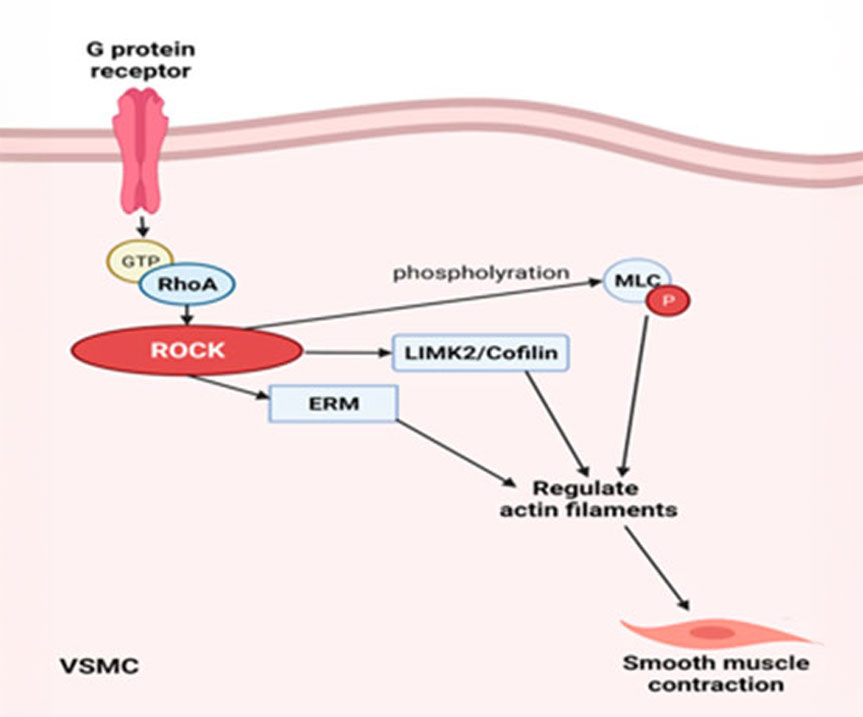
BCD101 is an innovative next-generation ROCK inhibitor that addresses the underlying causes of aging-related diseases.
It modulates the RhoA-ROCK pathway, which plays a key role in cell contraction, migration, and proliferation, thereby suppressing excessive cell contraction, inflammatory responses, and fibrosis that occur during the aging process.


- BCD101, the key ingredient of G-Care, is a herbal composition whose efficacy has been validated through over 10 years of clinical practice and research by a practicing Korean medicine doctor.
- The technology establishing the herbal extraction conditions has been patented for improving blood circulation
(Patent No. 10-2684027), ensuring both safety and reliability.

Nocturnal leg cramps, NLC
Nocturnal leg cramps (NLC) are sudden, painful muscle contractions that primarily occur in the legs, especially the calves. They often arise during sleep at night, disrupting rest due to the associated pain. NLC is a common condition, affecting approximately 40% of adults over 40 and about 7% of adolescents, and is particularly significant in the elderly as it contributes to leg discomfort.
Causes
- Aging
- Reduced vascular elasticity
- Decline in estrogen levels in menopausal women
Effects
- Sleep disturbances, fatigue, decreased concentration, and impaired daily functioning, leading to reduced quality of life
- In elderly patients, sudden posture changes after night cramps increase the risk of falls and secondary injuries
Current Treatment Status
01. Existing Treatments
02. Limitations
- There is currently no officially approved treatment for NLC, so management mainly relies on OTC products with combined functional ingredients.
03. Quinine Case
- Although some past studies reported effectiveness, quinine is no longer recommended for NLC due to serious side effects such as arrhythmia, thrombocytopenia, and hypersensitivity.
- The U.S. FDA has discontinued its use for NLC treatment.
04. Unmet Needs
- All existing treatments have limitations, creating a continued demand for safe and effective new therapies.
NLC, first in class
- No Approved Prescription Drugs
for NLC to Date
- Effects of Drugs like Phenytoin Reported,
but Development Limited
Kim et al., “Phenytoin in Night Muscle Cramps,”
J Korean Neurol Assoc, 2014
- Quinine – FDA Approval Withdrawn
Due to Serious Side Effects
Cochrane Review. Quinine for muscle cramps.
Cochrance Database Syst Rev. 2015.
- BICHEDAM BCD101
– Safe & Effective NLC Therapy Leading the Early Market
Innovative therapy combining Korean medicine
and modern science
introducing a new treatment paradigm
and leading the global bio-health market.
BICHEDAM Co., Ltd.
Head Office
Room 321, Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Research Center,
280 Daehak-ro, Gyeongsan-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea
Branch Office
Room 1516, Sky Valley 5th Building, 416 Hwagok-ro, Gangseo-gu, Seoul, Korea
CEO Hobin Moon
Email admin@bichedam.org
© 2025 BICHEDAM. All Rights Reserved.